
本文共 9397 字,大约阅读时间需要 31 分钟。
目录
第六章 配置文件
6.1 properties文件
application.properties。用法同以前的properties文件。
6.2 yaml
6.2.1 简介
YAML是 "YAML Ain't Markup Language"(YAML 不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:"Yet Another Markup Language"(仍是一种标记语言)。
非常适合用来做以数据为中心的配置文件
以后推荐使用这种yaml文件形式。
如果application.properties文件和yaml文件同时配置了同一种属性,那么会优先选择properties文件中的属性取值。
6.2.2 基本语法
- key: value; key和value之间有个空格。
- 大小写敏感。
- 使用缩进表示层级关系。
- 缩进不允许使用tab,只允许空格。
- 缩进的空格数不重要,只要相同层级的元素左对齐即可。
- #表示注释。
- 字符串无需加引号,如果要加,''(单引号)与""(双引号)表示字符串内容会被转义/不转义。

6.2.3 数据类型
- 字面量:单个的、不可再分的值。date、boolean、string、number、null
k: v
- 对象:键值对的集合。map、hash、set、object
行内写法: k: {k1:v1,k2:v2,k3:v3}
#或 k: k1: v1 k2: v2 k3: v3
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值。array、list、queue
行内写法: k: [v1,v2,v3]
#或者 k: - v1 - v2 - v3
6.2.4 示例
java实现的类:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")@Component@ToString@Datapublic class Person { private String userName; private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Integer age; private Pet pet; private String[] interests; private List animal; private Map score; private Set salarys; private Map > allPets;}@ToString@Datapublic class Pet { private String name; private Double weight;} yaml实现(application.yml,文件后缀名可以是yaml,也可以只写yml):
# yaml表示以上对象person: userName: zhangsan boss: false birth: 2019/12/12 20:12:33 age: 18 pet: name: tomcat weight: 23.4 interests: [篮球,游泳] animal: - jerry - mario # score: # english: 80 # math: 90 score: {english: 80,math: 90} salarys: [3999,4999.98,5999.99] allPets: sick: - {name: tom,weight: 24} - name: jerry weight: 47 health: [{name: mario,weight: 47}] 6.3 配置提示
自定义的类和配置文件绑定时一般没有提示,此时可以加入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
并且在打包时不要把这个依赖也带上,因为与业务无关:
<build>
<plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <excludes> <exclude> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> </exclude> </excludes> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
第七章 Web开发
7.1 SpringMVC自动配置概览
SpringBoot是框架的框架,底层的web开发仍旧是SpringMVC的所有功能,SpringBoot对SpringMVC做了很多自动配置。
SpringBoot对SpringMVC实现了哪些自动配置:
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most
applications.(大多场景我们都无需自定义配置)
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
- Inclusion of
ContentNegotiatingViewResolverandBeanNameViewResolverbeans.- 内容协商视图解析器和BeanName视图解析器
- Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (covered )).
- 静态资源(包括webjars)
- Automatic registration of
Converter,GenericConverter, andFormatterbeans.- 自动注册
Converter,GenericConverter,Formatter
- 自动注册
- Support for
HttpMessageConverters(covered ).- 支持
HttpMessageConverters(后来我们配合内容协商理解原理)
- 支持
- Automatic registration of
MessageCodesResolver(covered ).- 自动注册
MessageCodesResolver(国际化用)
- 自动注册
- Static
index.htmlsupport.- 静态index.html页支持(欢迎页)
- Custom
Faviconsupport (covered ).- 自定义
Favicon
- 自定义
- Automatic use of a
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializerbean (covered ).- 自动使用
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer(DataBinder负责将请求数据绑定到JavaBean上)
- 自动使用
7.2 简单功能分析
7.2.1 静态资源访问
7.2.1.1 静态资源目录
只要把静态资源文件放在类路径下:
①/static
②/public
③/resources
④/META-INF/resources
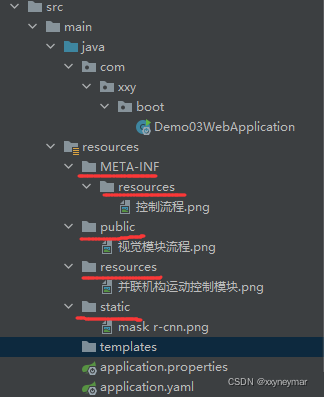
访问静态资源文件:当前项目根路径/ + 静态资源名
比如:
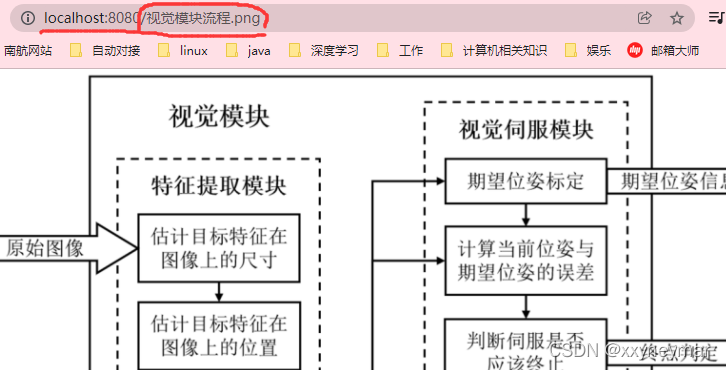
原理:静态映射/**。(**表示根路径下的所有文件夹及其子文件夹)
请求进来,先去找Controller看能不能处理,不能处理的所有请求又都交给静态资源处理器。
静态资源也找不到则响应404页面。
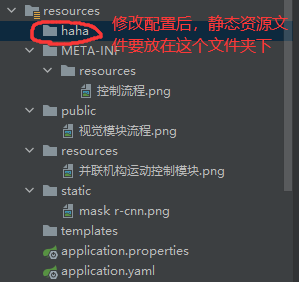
改变默认的静态资源路径:再yaml文件中修改属性。让其不在这四个默认路径下找静态资源文件。
spring: mvc: static-path-pattern: /res/** web: resources: static-locations: [classpath:/haha]
7.2.1.2 静态资源访问前缀
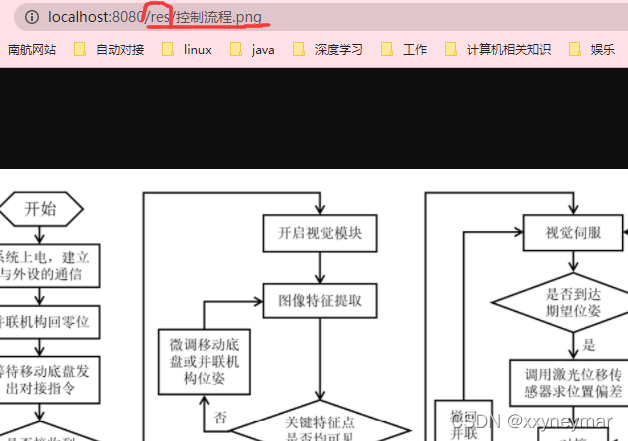
默认情况下是无前缀的。因为后续的拦截器等功能,为了防止静态资源也被拦截,一般都会修改这个默认的静态映射/**,给静态资源访问加一个前缀。
在yaml文件中修改:
spring: mvc: static-path-pattern: /res/**
当前项目 + static-path-pattern + 静态资源名 = 静态资源文件夹下找:
7.2.1.3 webjar
自动映射/webjars/**。
webjar官网:
比如jquery,有依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId> <artifactId>jquery</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> </dependency>
访问地址: 后面地址要按照依赖里面的包
路径。
7.2.2 欢迎页支持
两种方式:
- 静态资源路径下index.html
- 可以配置静态资源路径
- 但是不可以配置静态资源路径的访问前缀,否则导致index.html不能被默认访问
spring:# mvc:# static-path-pattern: /res/** 这个会导致welcome page功能失效 web: resources: static-locations: [classpath:/haha/]
- 创建能处理/index请求的controller
7.2.3 自定义Favicon
favicon即网站的图标。
favicon.ico 放在静态资源目录下即可,但是也不可以配置前缀。
spring:# mvc:# static-path-pattern: /res/** 这个会导致Favicon功能失效
7.2.4 静态资源配置原理
- SpringBoot启动默认加载 xxxAutoConfiguration 类(自动配置类)
- SpringMVC功能的自动配置类 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 生效
@Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false)@ConditionalOnWebApplication( type = Type.SERVLET)@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class})@ConditionalOnMissingBean({WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class})@AutoConfigureOrder(-2147483638)@AutoConfigureAfter({DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class})public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {} - 给容器中配置的重要内容:WebMvcAutoConfiguration中的一个静态类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
@Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false)@Import({WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class})@EnableConfigurationProperties({WebMvcProperties.class, WebProperties.class})@Order(0)public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer, ServletContextAware {} - 配置文件的相关属性和xxx进行了绑定。WebMvcProperties==spring.mvc、WebProperties==spring.web
@ConfigurationProperties( prefix = "spring.mvc")public class WebMvcProperties {}@ConfigurationProperties("spring.web")public class WebProperties {} - 这个配置类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter只有一个有参构造器。
//有参构造器所有参数的值都会从容器中确定//WebProperties webProperties 获取和spring.web绑定的所有的值的对象//WebMvcProperties mvcProperties 获取和spring.mvc绑定的所有的值的对象//ListableBeanFactory beanFactory Spring的beanFactory//HttpMessageConverters 找到所有的HttpMessageConverters//ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer 找到 资源处理器的自定义器。//DispatcherServletPath //ServletRegistrationBean 给应用注册Servlet、Filterpublic WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter(WebProperties webProperties, WebMvcProperties mvcProperties, ListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ObjectProvidermessageConvertersProvider, ObjectProvider resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider, ObjectProvider dispatcherServletPath, ObjectProvider > servletRegistrations) { this.resourceProperties = webProperties.getResources(); this.mvcProperties = mvcProperties; this.beanFactory = beanFactory; this.messageConvertersProvider = messageConvertersProvider; this.resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer = (WebMvcAutoConfiguration.ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer)resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider.getIfAvailable(); this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath; this.servletRegistrations = servletRegistrations; this.mvcProperties.checkConfiguration();}
- WebMvcAutoConfiguration中的关键方法addResourceHandler(),静态资源处理的默认规则:
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) { logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled"); } else { //访问webjars静态文件的规则 this.addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"); //访问静态资源 this.addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> { registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()); if (this.servletContext != null) { ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, "/"); registration.addResourceLocations(new Resource[]{resource}); } }); }} 上面代码中的isAddMappings()方法就通过一个boolean属性值的设置,如果设置为false,那
么就不会进入else,即会禁用所有静态资源规则。
spring: web: resources: add-mappings: false # 禁用所有静态资源文件规则
this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern()方法中得到的是静态映射/**:
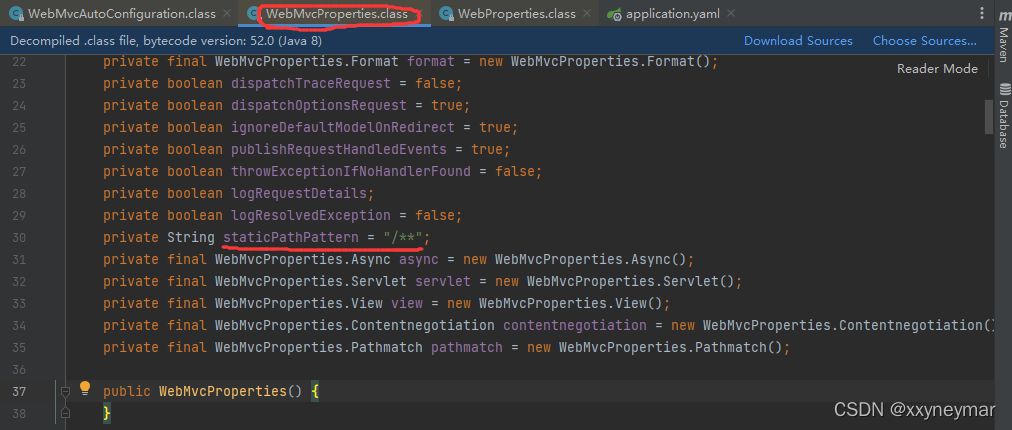
this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()方法中得到的是四种静态资源默认路径:

- WebMvcAutoConfiguration中的一个静态类EnableWebMvcConfiguration中的一个方法welcomePageHandlerMapping()定义了欢迎页的处理规则:
//HandlerMapping:处理器映射。保存了每一个Handler能处理哪些请求。 public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext, FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) { WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, this.getWelcomePage(), this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern()); welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(this.getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider)); welcomePageHandlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(this.getCorsConfigurations()); return welcomePageHandlerMapping;} WelcomePageHandlerMapping(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders, ApplicationContext applicationContext, Resource welcomePage, String staticPathPattern) { if (welcomePage != null && "/**".equals(staticPathPattern)) { logger.info("Adding welcome page: " + welcomePage); this.setRootViewName("forward:index.html"); } else if (this.welcomeTemplateExists(templateAvailabilityProviders, applicationContext)) { logger.info("Adding welcome page template: index"); this.setRootViewName("index"); }} 可以看出必须是/**,因此手动加了前缀的话,欢迎页功能就会失效。
PS:根据尚硅谷课程整理,如有侵权,联系删除
转载地址:https://blog.csdn.net/xxyneymar/article/details/122552775 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
关于作者
