
本文共 7836 字,大约阅读时间需要 26 分钟。
基于事件的 NIO 多线程服务器

黄林榕
2004 年 4 月 01 日发布
JDK1.4 的 NIO 有效解决了原有流式 IO 存在的线程开销的问题,在 NIO 中使用多线程,主要目的已不是为了应对每个客户端请求而分配独立的服务线程,而是通过多线程充分使用用多个 CPU 的处理能力和处理中的等待时间,达到提高服务能力的目的。
多线程的引入,容易为本来就略显复杂的 NIO 代码进一步降低可读性和可维护性。引入良好的设计模型,将不仅带来高性能、高可靠的代码,也将带来一个惬意的开发过程。
线程模型
NIO 的选择器采用了多路复用(Multiplexing)技术,可在一个选择器上处理多个套接字,
通过获取读写通道来进行 IO 操作。由于网络带宽等原因,在通道的读、写操作中是容易出现等待的,
所以在读、写操作中引入多线程,对性能提高明显,而且可以提高客户端的感知服务质量。所以本文的模型将主要通过使用读、写线程池
来提高与客户端的数据交换能力。
如下图所示,服务端接受客户端请求后,控制线程将该请求的读通道交给读线程池,由读线程池分配线程完成对客户端数据的读取操作;当读线程完成读操作后,将数据返回控制线程,进行服务端的业务处理;完成
业务处理后,将需回应给客户端的数据和写通道提交给写线程池,由写线程完成向客户端发送回应数据的操作。
(NIO 多线程服务器模型)
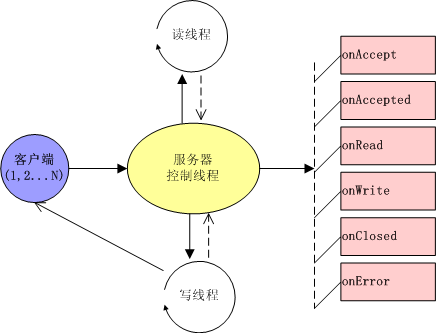

同时整个服务端的流程处理,建立于事件机制上。在
[接受连接->读->业务处理->写
->关闭连接
]这个
过程中,触发器将触发相应事件,由事件处理器对相应事件分别响应,完成服务器端的业务处理。
下面我们就来详细看一下这个模型的各个组成部分。
相关事件定义 在这个模型中,我们定义了一些基本的事件:
(1)onAccept:当服务端收到客户端连接请求时,触发该事件。通过该事件我们可以知道有新的客户端呼入。该事件可用来控制服务端的负载。例如,服务器可设定同时只为一定数量客户端提供服务,当同时请求数超出数量时,可在响应该事件时直接抛出异常,以拒绝新的连接。
(2)onAccepted:当客户端请求被服务器接受后触发该事件。该事件表明一个新的客户端与服务器正式建立连接。
(3)onRead:当客户端发来数据,并已被服务器控制线程正确读取时,触发该事件
。该事件通知各事件处理器可以对客户端发来的数据进行实际处理了。需要注意的是,在本模型中,客户端的数据读取是由控制线程交由读线程完成的,事件处理器不需要在该事件中进行专门的读操作,而只需将控制线程传来的数据进行直接处理即可。
(4)onWrite:当客户端可以开始接受服务端发送数据时触发该事件,通过该事件,我们可以向客户端发送回应数据。
在本模型中,事件处理器只需要在该事件中设置
(5)onClosed:当客户端与服务器断开连接时触发该事件。
(6)onError:当客户端与服务器从连接开始到最后断开连接期间发生错误时触发该事件。通过该事件我们可以知道有什么错误发生。
事件回调机制的实现
在这个模型中,事件采用广播方式,也就是所有在册的事件处理器都能获得事件通知。这样可以将不同性质的业务处理,分别用不同的处理器实现,使每个处理器的业务功能尽可能单一。
如下图:整个事件模型由监听器、事件适配器、事件触发器、事件处理器组成。
(事件模型)
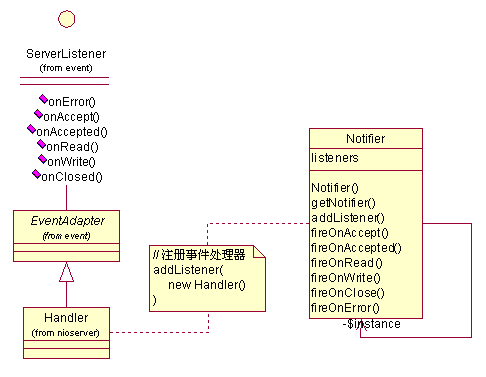
 监听器(Serverlistener):这是一个事件接口,定义需监听的服务器事件,如果您需要定义更多的事件,可在这里进行扩展。
监听器(Serverlistener):这是一个事件接口,定义需监听的服务器事件,如果您需要定义更多的事件,可在这里进行扩展。
public interface Serverlistener {
public void onError(String error);
public void onAccept() throws Exception;
public void onAccepted(Request request) throws Exception;
public void onRead(Request request) throws Exception;
public void onWrite(Request request, Response response) throws Exception;
public void onClosed(Request request) throws Exception;
}
事件适配器(EventAdapter):对 Serverlistener 接口实现一个适配器 (EventAdapter),这样的好处是最终的事件处理器可以只处理所关心的事件。
public abstract class EventAdapter implements Serverlistener {
public EventAdapter() {
}
public void onError(String error) {}
public void onAccept() throws Exception {}
public void onAccepted(Request request) throws Exception {}
public void onRead(Request request) throws Exception {}
public void onWrite(Request request, Response response) throws Exception {}
public void onClosed(Request request) throws Exception {}
}
事件触发器(Notifier):用于在适当的时候通过触发服务器事件,通知在册的事件处理器对事件做出响应。触发器以 Singleton 模式实现,统一控制整个服务器端的事件,避免造成混乱。
public class Notifier {
private static Arraylist listeners = null;
private static Notifier instance = null;
private Notifier() {
listeners = new Arraylist();
}
/**
* 获取事件触发器
* @return 返回事件触发器
*/
public static synchronized Notifier getNotifier() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Notifier();
return instance;
}
else return instance;
}
/**
* 添加事件监听器
* @param l 监听器
*/
public void addlistener(Serverlistener l) {
synchronized (listeners) {
if (!listeners.contains(l))
listeners.add(l);
}
}
public void fireOnAccept() throws Exception {
for (int i = listeners.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
( (Serverlistener) listeners.get(i)).onAccept();
}
....// other fire method
}
事件处理器(Handler):继承事件适配器,对感兴趣的事件进行响应处理,实现业务处理。以下是一个简单的事件处理器实现,它响应 onRead 事件,在终端打印出从客户端读取的数据。
public class ServerHandler extends EventAdapter {
public ServerHandler() {
}
public void onRead(Request request) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Received: " + new String(data));
}
}
事件处理器的注册。为了能让事件处理器获得服务线程的事件通知,事件处理器需在触发器中注册。
ServerHandler handler = new ServerHandler();
Notifier.addlistener(handler);
实现 NIO 多线程服务器
NIO 多线程服务器主要由主控服务线程、读线程和写线程组成。
(线程模型)
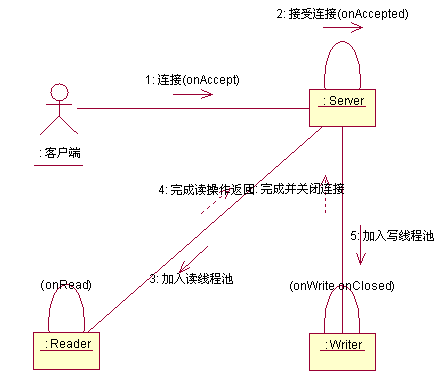
 主控服务线程(Server):主控线程将创建读、写线程池,实现监听、接受客户端请求,同时将读、写通道提交由相应的读线程(Reader)和写服务线程 (Writer)
主控服务线程(Server):主控线程将创建读、写线程池,实现监听、接受客户端请求,同时将读、写通道提交由相应的读线程(Reader)和写服务线程 (Writer)
,由读写线程分别完成对客户端数据的读取和对客户端的回应操作。
public class Server implements Runnable {
....
private static int MAX_THREADS = 4;
public Server(int port) throws Exception {
....
// 创建无阻塞网络套接
selector = Selector.open();
sschannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
sschannel.configureBlocking(false);
address = new InetSocketAddress(port);
ServerSocket ss = sschannel.socket();
ss.bind(address);
sschannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("Server started ...");
System.out.println("Server listening on port: " + port);
// 监听
while (true) {
try {
int num = 0;
num = selector.select();
if (num > 0) {
Set selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator it = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) it.next();
it.remove();
// 处理 IO 事件
if ( (key.readyOps() & SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) ==
SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) {
// Accept the new connection
ServerSocketChannel ssc =
(ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
notifier.fireOnAccept();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
// 触发接受连接事件
Request request = new Request(sc);
notifier.fireOnAccepted(request);
// 注册读操作 , 以进行下一步的读操作
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, request);
}
else if ( (key.readyOps() & SelectionKey.OP_READ) ==
SelectionKey.OP_READ ) {
// 提交读服务线程读取客户端数据
Reader.processRequest(key);
key.cancel();
}
else if ( (key.readyOps() & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) ==
SelectionKey.OP_WRITE ) {
// 提交写服务线程向客户端发送回应数据
Writer.processRequest(key);
key.cancel();
}
}
}
else {
addRegister(); // 在 Selector 中注册新的写通道
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
notifier.fireOnError("Error occured in Server: " + e.getMessage());
continue;
}
}
}
....
}
读线程(Reader):使用线程池技术,通过多个线程读取客户端数据,以充分利用网络数据传输的时间,提高读取效率。
public class Reader extends Thread {
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
SelectionKey key;
synchronized (pool) {
while (pool.isEmpty()) {
pool.wait();
}
key = (SelectionKey) pool.remove(0);
}
// 读取客户端数据,并触发 onRead 事件
read(key);
}
catch (Exception e) {
continue;
}
}
}
....
}
写线程(Writer):和读操作一样,使用线程池,负责将服务器端的数据发送回客户端。
public final class Writer extends Thread {
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
SelectionKey key;
synchronized (pool) {
while (pool.isEmpty()) {
pool.wait();
}
key = (SelectionKey) pool.remove(0);
}
// 向客户端发送数据,然后关闭连接,并分别触发 onWrite,onClosed 事件
write(key);
}
catch (Exception e) {
continue;
}
}
}
....
}
具体应用
NIO 多线程模型的实现告一段落,现在我们可以暂且将 NIO 的各个 API 和烦琐的调用方法抛于脑后,专心于我们的实际应用中。
我们用一个简单的 TimeServer(时间查询服务器)来看看该模型能带来多么简洁的开发方式。
在这个 TimeServer 中,将提供两种语言(中文、英文)的时间查询服务。我们将读取客户端的查询命令(GB/EN),并回应相应语言格式的当前时间。在应答客户的请求的同时,服务器将进行日志记录。做为示例,对日志记录,我们只是简单地将客户端的访问时间和 IP 地址输出到服务器的终端上。实现时间查询服务的事件处理器(TimeHandler):
public class TimeHandler extends EventAdapter {
public TimeHandler() {
}
public void onWrite(Request request, Response response) throws Exception {
String command = new String(request.getDataInput());
String time = null;
Date date = new Date();
// 判断查询命令
if (command.equals("GB")) {
// 中文格式
DateFormat cnDate = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.FulL,
DateFormat.FulL, Locale.CHINA);
time = cnDate.format(date);
}
else {
// 英文格式
DateFormat enDate = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.FulL,
DateFormat.FulL, Locale.US);
time = enDate.format(date);
}
response.send(time.getBytes());
}
}
实现日志记录服务的事件处理器(LogHandler):
public class LogHandler extends EventAdapter {
public LogHandler() {
}
public void onClosed(Request request) throws Exception {
String log = new Date().toString() + " from " + request.getAddress()
.toString();
System.out.println(log);
}
public void onError(String error) {
System.out.println("Error: " + error);
}
}
启动程序:
public class Start {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
LogHandler loger = new LogHandler();
TimeHandler timer = new TimeHandler();
Notifier notifier = Notifier.getNotifier();
notifier.addlistener(loger);
notifier.addlistener(timer);
System.out.println("Server starting ...");
Server server = new Server(5100);
Thread tServer = new Thread(server);
tServer.start();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Server error: " + e.getMessage());
System.exit(-1);
}
}
}
小结
通过例子我们可以看到,基于事件回调的 NIO 多线程服务器模型,提供了清晰直观的实现方式,可让开发者从 NIO 及多线程的技术细节中摆脱出来,集中精力关注具体的业务实现。
附录
相关主题“
Merlin 给 Java 平台带来了非阻塞 I/O”(
developerWorks,2002 年 3 月)。
转载地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_32601635/article/details/114067773 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
关于作者
