
本文共 16183 字,大约阅读时间需要 53 分钟。
==学习目标==
1、能够了解红黑树
2、能够掌握HashSet集合的特点以及使用(特点以及使用,哈希表数据结构)
3、能够掌握Map集合的特点以及使用(特点,常见方法,Map集合的遍历)
4、能够掌握HashMap集合的特点以及使用
5、能够掌握TreeMap集合的特点以及使用
==知识点==
- 红黑树
- HashSet
- Map
- HashMap
- TreeMap
==知识点梳理==
==超详细讲义==
1.红黑树
1.1红黑树-概述【了解】
1.什么是红黑树
平衡二叉B树,每一个节点可以是红或者黑,红黑树不是 高度平衡 的,它的平衡是通过"自己的红黑规则"进行实现的。
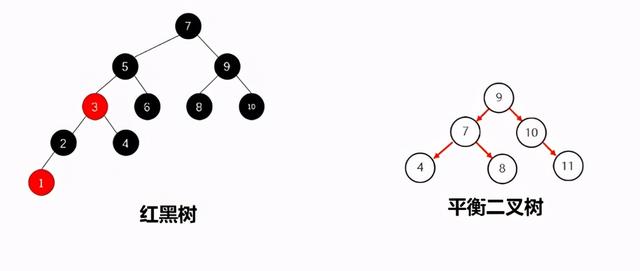
1.2 红黑树-红黑规则 (了解)
- 红黑树的红黑规则有哪些每一个节点或是红色的,或者是黑色的根节点必须是黑色所有叶子节点(空的节点被称作叶子节点)都是黑色的不能出现两个红色节点相连 的情况对每一个节点,从该节点到其所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色节点
1.3 红黑树-添加节点的默认颜色(了解)
添加节点时,默认为红色,效率高
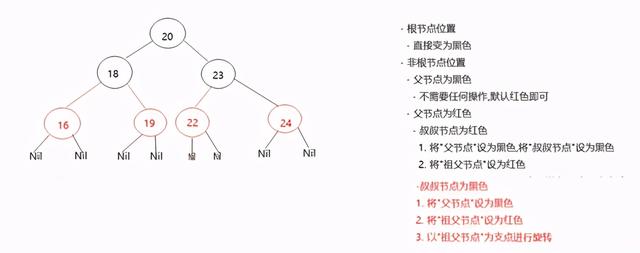
1.4 红黑树-添加节点后,如何保证红黑规则1 【难点】
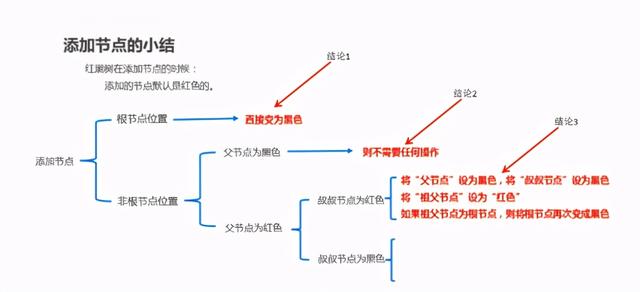

1.5 红黑树-添加节点后,如何保证红黑规则2 【难点】
(旋转之后,根据规则验证是否是红黑树,总结红黑树添加节点的规则)
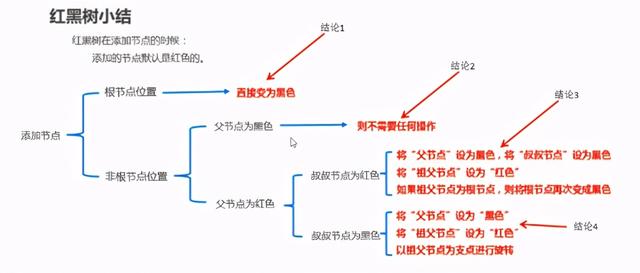
1.6 红黑树练习-成绩排序案例【重点】
(共3点)
1.案例需求
- 用TreeSet集合存储多个学生信息(姓名,语文成绩,数学成绩,英语成绩),并遍历该集合
- 要求: 按照总分从低到高排序
代码实现
学生类
public class Student implements Comparable { private String name; private int chinese; private int math; private int english; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int chinese, int math, int english) { this.name = name; this.chinese = chinese; this.math = math; this.english = english; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getChinese() { return chinese; } public void setChinese(int chinese) { this.chinese = chinese; } public int getMath() { return math; } public void setMath(int math) { this.math = math; } public int getEnglish() { return english; } public void setEnglish(int english) { this.english = english; } public int getSum() { return this.chinese + this.math + this.english; } @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { // 主要条件: 按照总分进行排序 int result = o.getSum() - this.getSum(); // 次要条件: 如果总分一样,就按照语文成绩排序 result = result == 0 ? o.getChinese() - this.getChinese() : result; // 如果语文成绩也一样,就按照数学成绩排序 result = result == 0 ? o.getMath() - this.getMath() : result; // 如果总分一样,各科成绩也都一样,就按照姓名排序 result = result == 0 ? o.getName().compareTo(this.getName()) : result; return result; }} 测试类
public class TreeSetDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建TreeSet集合对象,通过比较器排序进行排序 TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(); //创建学生对象 Student s1 = new Student("jack", 98, 100, 95); Student s2 = new Student("rose", 95, 95, 95); Student s3 = new Student("sam", 100, 93, 98); //把学生对象添加到集合 ts.add(s1); ts.add(s2); ts.add(s3); //遍历集合 for (Student s : ts) { System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getChinese() + "," + s.getMath() + "," + s.getEnglish() + "," + s.getSum()); } }} 2.TreeSet原理
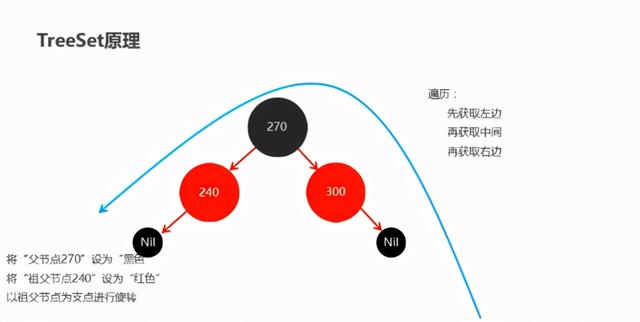

2.HashSet集合
2.1HashSet-基本使用【重点】
1.什么是HashSet(HashSet的特点)
- 底层数据结构是哈希表
- 存取无序
- 不可以存储重复元素
- 没有索引,不能使用普通for循环遍历(get方法)
2.HashSet使用-存储字符串并遍历
package com.itheima.myhashset;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;/** * 添加字符串并进行遍历 */public class HashSetDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet hs = new HashSet<>(); hs.add("hello"); hs.add("world"); hs.add("java"); hs.add("java"); hs.add("java"); hs.add("java"); hs.add("java"); hs.add("java"); Iterator it = hs.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ String s = it.next(); System.out.println(s); } System.out.println("============================="); for (String s : hs) { System.out.println(s); } }} 2.2哈希值【了解】
1.什么是哈希值
是JDK根据对象的地址或者属性值,算出来的int类型的整数
2.如何获取对象中的Hash值
Object类中有一个方法: public int hashCode():根据对象的地址值计算出来的哈希值
3.哈希值的特点
- 没有重写HashCode的情况:
1.同种一对象多次调用hashCode方法返回值是一样的
2.不同对象hashCode方法返回值不一样
- Object子类重写hashCode方法的情况:
重写的目的是计算对象哈希值时,按属性值来计算,因此只要属性值相同,不同对象的hashCode方法返回值是一样的
package com.itheima.myhashset;/** * 计算哈希值 */public class HashSetDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student("xiaozhi",23); Student s2 = new Student("xiaomei",22); //因为在Object类中,是根据对象的地址值计算出来的哈希值。 System.out.println(s1.hashCode());//1060830840 System.out.println(s1.hashCode());//1060830840 System.out.println(s2.hashCode());//2137211482 }} Student类
package com.itheima.myhashset;public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } //我们可以对Object类中的hashCode方法进行重写 //在重写之后,就一般是根据对象的属性值来计算哈希值的。 //此时跟对象的地址值就没有任何关系了。 @Override public int hashCode() { int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0; result = 31 * result + age; return result; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + ''' + ", age=" + age + '}'; }} 2.4HashSet-JDK7底层原理【难点】
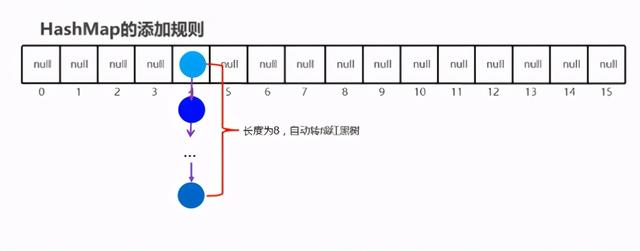
哈希表=数组 + 链表
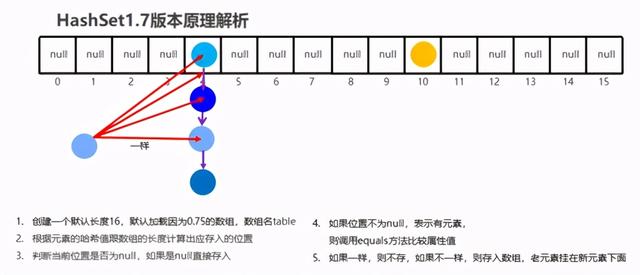
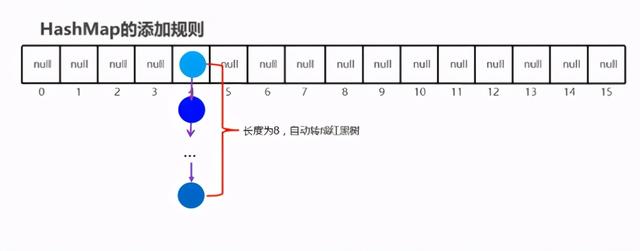
2.5HashSet-JDK8底层优化【难点】
(共两点)
1.HashSet 在JDK1.8之后的原理
- 节点个数少于等于8个数组 + 链表
- 节点个数多于8个数组 + 红黑树
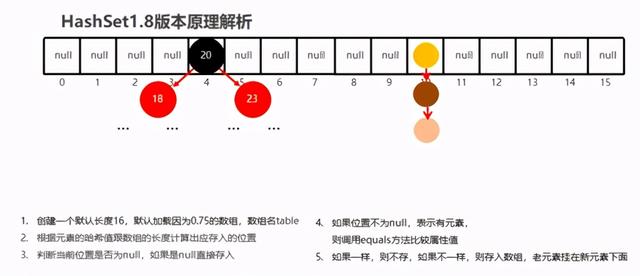
2.HashSet 在JDK1.8版本的存储流程
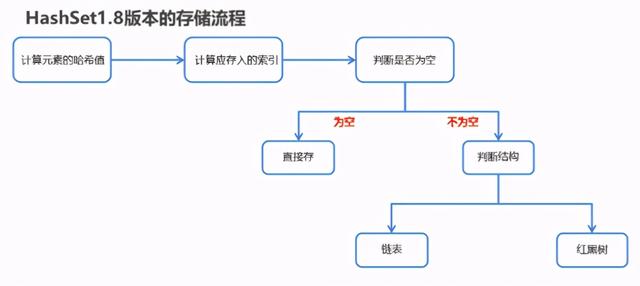
2.6HashSet集合存储学生对象并遍历【重点】
- 案例需求创建一个存储学生对象的集合,存储多个学生对象,使用程序实现在控制台遍历该集合
- 要求:学生对象的成员变量值相同,我们就认为是同一个对象
代码实现
测试类
public class HashSetDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //HashSet集合存储自定义类型元素,要想实现元素的唯一,要求必须重写hashCode方法和equals方法 HashSet hashSet = new HashSet<>(); Student s1 = new Student("xiaohei",23); Student s2 = new Student("xiaohei",23); Student s3 = new Student("xiaomei",22); hashSet.add(s1); hashSet.add(s2); hashSet.add(s3); for (Student student : hashSet) { System.out.println(student); } }} 学生类
package com.itheima.myhashset;public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) { return true; } if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) { return false; } Student student = (Student) o; if (age != student.age) { return false; } return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null; } //我们可以对Object类中的hashCode方法进行重写 //在重写之后,就一般是根据对象的属性值来计算哈希值的。 //此时跟对象的地址值就没有任何关系了。 @Override public int hashCode() { int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0; result = 31 * result + age; return result; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + ''' + ", age=" + age + '}'; }} 3.Map集合
3.1Map-基本使用【重点、难点】
(共3点)
1.什么是Map集合【记忆】
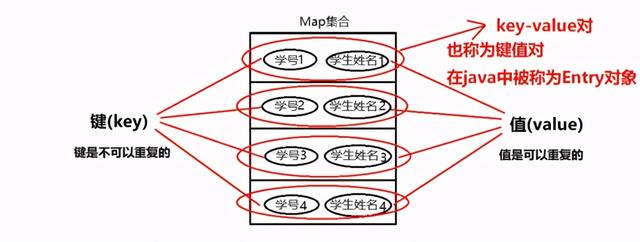
Map集合又称为双列集合,双列集合中元素的内容是成对的
2.Map集合的特点 【记忆】
键不能重复,值可以重复
键与值之间是一一对应的关系
(键+值)这个整体我们称之为"键值对"或"键值对对象",在Java中又叫"Entry对象"
3.如何使用Map集合
1.Map集合格式
interface Map K:键的类型;V:值的类型
2.如何创建Map集合对象
Map map = new HashMap();//使用具体实现类,采用多态形式创建
4.使用Map集合存储学生学号和姓名
package com.itheima.mapdemo1;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;/** * Map的基本使用 */public class MyMap1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new HashMap<>(); //map.add(); map.put("itheima001","小智"); map.put("itheima002","小美"); map.put("itheima003","大胖"); System.out.println(map); }} 3.2Map常用方法【重点】
方法介绍
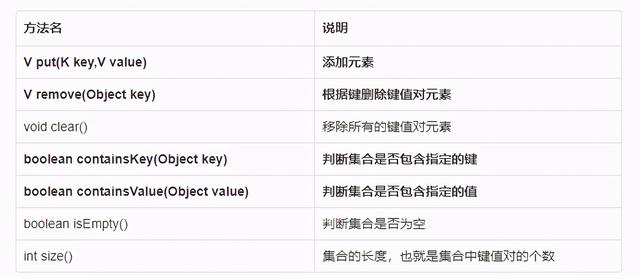
示例代码
package com.itheima.mapdemo1;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;/** * Map的基本方法 */public class MyMap2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("itheima001","小智"); map.put("itheima002","小美"); map.put("itheima003","大胖"); map.put("itheima004","小黑"); map.put("itheima005","大师"); //method1(map); //method2(map); //method3(map); //method4(map); //method5(map); //method6(map); //method7(map); } private static void method7(Map map) { // int size() 集合的长度,也就是集合中键值对的个数 int size = map.size(); System.out.println(size); } private static void method6(Map map) { // boolean isEmpty() 判断集合是否为空 boolean empty1 = map.isEmpty(); System.out.println(empty1);//false map.clear(); boolean empty2 = map.isEmpty(); System.out.println(empty2);//true } private static void method5(Map map) { // boolean containsValue(Object value) 判断集合是否包含指定的值 boolean result1 = map.containsValue("aaa"); boolean result2 = map.containsValue("小智"); System.out.println(result1); System.out.println(result2); } private static void method4(Map map) { // boolean containsKey(Object key) 判断集合是否包含指定的键 boolean result1 = map.containsKey("itheima001"); boolean result2 = map.containsKey("itheima006"); System.out.println(result1); System.out.println(result2); } private static void method3(Map map) { // void clear() 移除所有的键值对元素 map.clear(); System.out.println(map); } private static void method2(Map map) { // V remove(Object key) 根据键删除键值对元素 String s = map.remove("itheima001"); System.out.println(s); System.out.println(map); } private static void method1(Map map) { // V put(K key,V value) 添加元素 //如果要添加的键不存在,那么会把键值对都添加到集合中 //如果要添加的键是存在的,那么会覆盖原先的值,把原先值当做返回值进行返回。 String s = map.put("itheima001", "aaa"); System.out.println(s); System.out.println(map); }} 3.3Map-第一种遍历方式【重点】
方法介绍
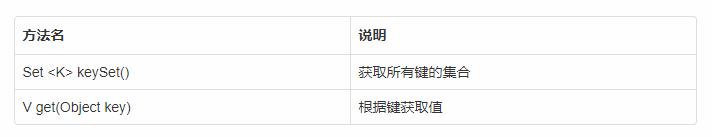
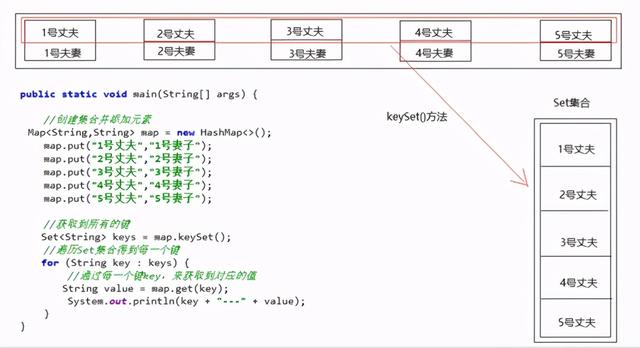
示例代码
package com.itheima.mapdemo1;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Set;/** * Map的第一种遍历方式 */public class MyMap3 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合并添加元素 Map map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("1号丈夫","1号妻子"); map.put("2号丈夫","2号妻子"); map.put("3号丈夫","3号妻子"); map.put("4号丈夫","4号妻子"); map.put("5号丈夫","5号妻子"); //获取到所有的键 Set keys = map.keySet(); //遍历Set集合得到每一个键 for (String key : keys) { //通过每一个键key,来获取到对应的值 String value = map.get(key); System.out.println(key + "---" + value); } }} 3.4Map-第二种遍历方式【重点】
方法介绍
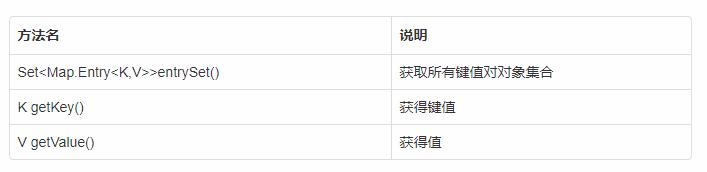
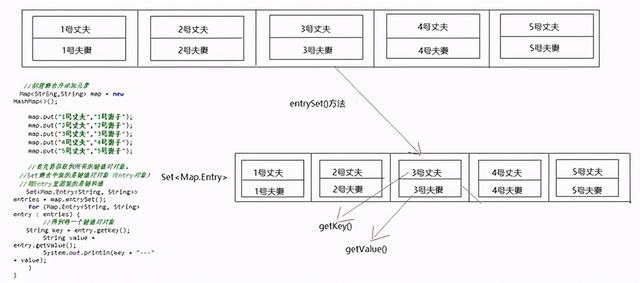
示例代码
package com.itheima.mapdemo1;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Set;/** * Map的第二种遍历方式 */public class MyMap4 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合并添加元素 Map map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("1号丈夫","1号妻子"); map.put("2号丈夫","2号妻子"); map.put("3号丈夫","3号妻子"); map.put("4号丈夫","4号妻子"); map.put("5号丈夫","5号妻子"); //首先要获取到所有的键值对对象。 //Set集合中装的是键值对对象(Entry对象) //而Entry里面装的是键和值 Set> entries = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry entry : entries) { //得到每一个键值对对象 String key = entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key + "---" + value); } }} 4.HashMap集合
4.1HashMap-原理解析【难点】
1.HashMap小结
- HashMap底层是哈希表结构
- 依赖hashCode方法和equals方法保证键的唯一
- 如果键要存储自定义对象,需要重写hashCode和equals方法
4.2 HashMap集合-练习【重点】
(共4点,第4点是对forEache的解析)
1.案例需求
- 创建一个HashMap集合,键是学生对象(Student),值是籍贯 (String)。存储三个元素,并遍历。
- 要求保证键的唯一性:如果学生对象的成员变量值相同,我们就认为是同一个对象
2.实现思路
- 定义学生类
- 创建HashMap集合对象
- 添加学生对象
- 为了保证key的一致性,重写学生类的hashCode和equals方法
3.代码实现
学生类
package com.itheima.mapdemo1;public class Student{ private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Student student = (Student) o; if (age != student.age) return false; return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null; } @Override public int hashCode() { int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0; result = 31 * result + age; return result; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + ''' + ", age=" + age + '}'; }} 测试类
package com.itheima.mapdemo1;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Set;/** * Map的练习 */public class MyMap5 { public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap hm = new HashMap<>(); Student s1 = new Student("xiaohei",23); Student s2 = new Student("dapang",22); Student s3 = new Student("xiaomei",22); hm.put(s1,"江苏"); hm.put(s2,"北京"); hm.put(s3,"天津"); //第一种:先获取到所有的键,再通过每一个键来找对应的值 Set keys = hm.keySet(); for (Student key : keys) { String value = hm.get(key); System.out.println(key + "----" + value); } System.out.println("==================================="); //第二种:先获取到所有的键值对对象。再获取到里面的每一个键和每一个值 Set> entries = hm.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry entry : entries) { Student key = entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key + "----" + value); } System.out.println("==================================="); //第三种: hm.forEach( (Student key, String value)->{ System.out.println(key + "----" + value); } ); }} 4.forEach方法解析

5.TreeMap集合
5.1TreeMap-原理解析【了解】
1.TreeMap-小结
- TreeMap底层是红黑树结构
- 依赖自然排序或者比较器排序,对键进行排序
- 如果 键存储 的是自定义对象,需要实现Comparable接口或者在创建TreeMap对象时候给出比较器排序规则
5.2TreeMap集合应用案例【重点】
- 案例需求创建一个TreeMap集合,键是学生对象(Student),值是籍贯(String),学生属性姓名和年龄,按照年龄进行排序并遍历
- 要求按照学生的年龄进行排序,如果年龄相同则按照姓名进行排序
- 实现思路
1.创建学生类
2.创建TreeMap集合对象
3.创建学生对象
4.添加学生对象
5.遍历输出
- 代码实现
学生类
package com.itheima.maptest;public class Student/* implements Comparable*/{ private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + ''' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } /* @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { //按照年龄进行排序 int result = o.getAge() - this.getAge(); //次要条件,按照姓名排序。 result = result == 0 ? o.getName().compareTo(this.getName()) : result; return result; }*/} 测试类
package com.itheima.maptest;import java.util.Comparator;import java.util.TreeMap;/** * 需求:创建一个TreeMap集合,键是学生对象(Student),值是籍贯(String)。 * 学生属性姓名和年龄,按照年龄进行排序并遍历。 */public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { TreeMap tm = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { int result = o1.getAge() - o2.getAge(); result = result== 0 ? o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()) : result; return result; } }); Student s1 = new Student("xiaohei",23); Student s2 = new Student("dapang",22); Student s3 = new Student("xiaomei",22); tm.put(s1,"江苏"); tm.put(s2,"北京"); tm.put(s3,"天津"); tm.forEach( (Student key, String value)->{ System.out.println(key + "---" + value); } ); }} 转载地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_33305027/article/details/112124688 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
关于作者
