【Spring】Spring基础配置-AOP
发布日期:2021-06-29 13:38:33
浏览次数:2
分类:技术文章
本文共 4970 字,大约阅读时间需要 16 分钟。
转载请注明出处:
本文源自【】
分析
AOP: 面向切面编程,相对于OOP面向对象编程。
OOP: Object Oriented Programming,面向对象的程序设计。Spring的AOP的存在目的是为了解耦。AOP可以让一组类共享相同的行为。
在OOP中只能通过继承类和实现接口,来使代码的耦合度增强,且类继承只能为单继承,阻碍更多行为添加到一组类上,AOP弥补了OOP的不足。Spring支持AspectJ的注解式切面编程
1、使用@Aspect声明类是一个切面2、使用@After,@Before,@Around 定义建言(advice),可直接将拦截规则(切点)作为参数。3、其中@After,@Before,@Around参数的拦截规则为切点(PointCut),为了使切点复用,可使用@PointCut专门定义拦截规则,然后在@After,@Before,@Around的参数中调用4、其中符合条件的每一个被拦截处为连接点(JoinPoint)
本示例演示基于注解拦截和基于方法拦截两种方式,演示一种模拟记录操作的日志系统的实现。
其中注解式拦截能够很好地控制要拦截的粒度和获得更丰富的信息,Spring本身在事务处理(@Transcational)和数据缓存(@Cacheable等)上面都使用此种形式的拦截。
pom.xml的配置不再累赘写上。
不知道写的朋友请见此篇博客:示例
添加Spring aop支持及AspectJ依赖
org.springframework spring-aop 4.2.3.RELEASE org.aspectj aspectjrt 1.8.9 org.aspectj aspectjweaver 1.8.9
编写拦截规则的注解
package cn.hncu.p1_3_3_aop;import java.lang.annotation.*;/** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * User: 陈浩翔. * Date: 2016/11/9. * Time: 上午 11:11. * Explain:注解类 */@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documentedpublic @interface Action { String name();} 编写使用注解的被拦截类
package cn.hncu.p1_3_3_aop;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;/** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * User: 陈浩翔. * Date: 2016/11/9. * Time: 上午 11:16. * Explain:使用注解的被拦截类 */@Servicepublic class DemoAnnotationService { @Action(name = "@Action---DemoAnnotationService.add操作") public void add(){ System.out.println("DemoAnnotationService.add..."); }} 编写使用方法规则的被拦截类
package cn.hncu.p1_3_3_aop;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;/** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * User: 陈浩翔. * Date: 2016/11/9. * Time: 上午 11:23. * Explain:使用方法规则的被拦截类 */@Servicepublic class DemoMethodService { @Action(name="@Action---DemoMethodService.add操作") public void add(){ System.out.println("DemoMethodService.add..."); }} 编写切面
package cn.hncu.p1_3_3_aop;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.lang.reflect.Method;/** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * User: 陈浩翔. * Date: 2016/11/9. * Time: 上午 11:24. * Explain:切面 */@Aspect//通过@Aspect注解声明这是一个切面@Component//通过@Component让此切面成为Spring容器管理的Beanpublic class LogAspect { //注意这两个@Pointcut写法的区别!!! // 一个是拦截注解(写了@Action注解的方法都会被拦截),一个是拦截类方法 @Pointcut("@annotation(cn.hncu.p1_3_3_aop.Action)")//通过@PointCut注解声明切点 //@Pointcut("execution(* cn.hncu.p1_3_3_aop.DemoAnnotationService..*(..))") //配置切入点,该方法无方法体,主要为方便同类中其他方法使用此处配置的切入点 public void annotatiomPointCut(){ } //拦截注解 @After("annotatiomPointCut()")//通过@After注解声明一个建言,并使用@PointCut定义的切点 public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint){ MethodSignature signature =(MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature(); Method method = signature.getMethod(); Action action = method.getAnnotation(Action.class); System.out.println(action.name());//通过反射可获得注解上的属性,可以用来做日志记录等相关操作 } @Before("execution(* cn.hncu.p1_3_3_aop.DemoMethodService.*(..))") //通过@Before注解声明一个建言,此建言直接使用拦截规则作为参数 public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){ MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); Method method = signature.getMethod(); Action action = method.getAnnotation(Action.class); System.out.println("方法规则式拦截:" + method.getName()+" "+action.name()); }} 编写配置类
package cn.hncu.p1_3_3_aop;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;/** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * User: 陈浩翔. * Date: 2016/11/9. * Time: 上午 11:42. * Explain:配置类 */@Configuration@ComponentScan("cn.hncu.p1_3_3_aop")@EnableAspectJAutoProxy //使用@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解开启Spring对AspectJ代理的支持public class AopConfig { } 运行类
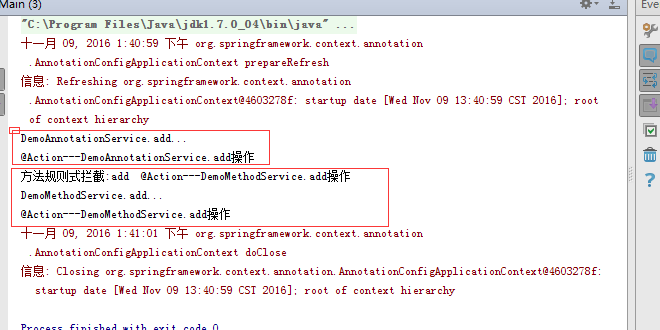
package cn.hncu.p1_3_3_aop;import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;/** * Created with IntelliJ IDEA. * User: 陈浩翔. * Date: 2016/11/9. * Time: 上午 11:41. * Explain:运行类 */public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AopConfig.class); DemoAnnotationService demoAnnotationService = context.getBean(DemoAnnotationService.class); demoAnnotationService.add(); DemoMethodService demoMethodService = context.getBean(DemoMethodService.class); demoMethodService.add(); context.close(); }} 运行结果
项目链接—具体包:
本文章由编写, 所有权利保留。
转载请注明出处:
本文源自【】
转载地址:https://chenhx.blog.csdn.net/article/details/53098650 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
网站不错 人气很旺了 加油
[***.192.178.218]2024年04月07日 22时33分25秒
关于作者

喝酒易醉,品茶养心,人生如梦,品茶悟道,何以解忧?唯有杜康!
-- 愿君每日到此一游!
推荐文章
linux i2c子系统abc
2019-04-29
CSS3 帧动画(Sprite,直译叫雪碧图)
2019-04-29
Java 父线程与子线程相互通信的方法
2019-04-29
Redis 六种淘汰策略和三种删除策略
2019-04-29
Java LinkedHashMap
2019-04-29
JPA 多线程同时对一条数据进行Update的问题
2019-04-29
JPA 多线程对数据进行更新,Update和Insert同时存在的问题
2019-04-29
Java 高性能队列Disruptor
2019-04-29
SpringBoot 使用https
2019-04-29
Java 读写锁
2019-04-29
JVM Minor GC、Full GC和Major GC
2019-04-29
SpringBoot @Scheduled 执行两次的问题
2019-04-29
tomcat配置JVM
2019-04-29
Ubuntu软件安装&卸载
2019-04-29
面试笔试易错知识点Java篇八
2019-04-29
弹性事务框架ETF4J——面向Java微服务的交易最终一致性解决方案
2019-04-29
【Scala 教程】Scala 条件与循环语句
2019-04-29
【Scala 教程】Scala 集合类型
2019-04-29
JAVA 线程同步机制 synchronized
2019-04-29