
python 数据科学 - 【回归分析】 ☞ 线性回归(2)

发布日期:2021-06-30 19:51:18
浏览次数:2
分类:技术文章
本文共 614 字,大约阅读时间需要 2 分钟。
资料:
回归模型估测:
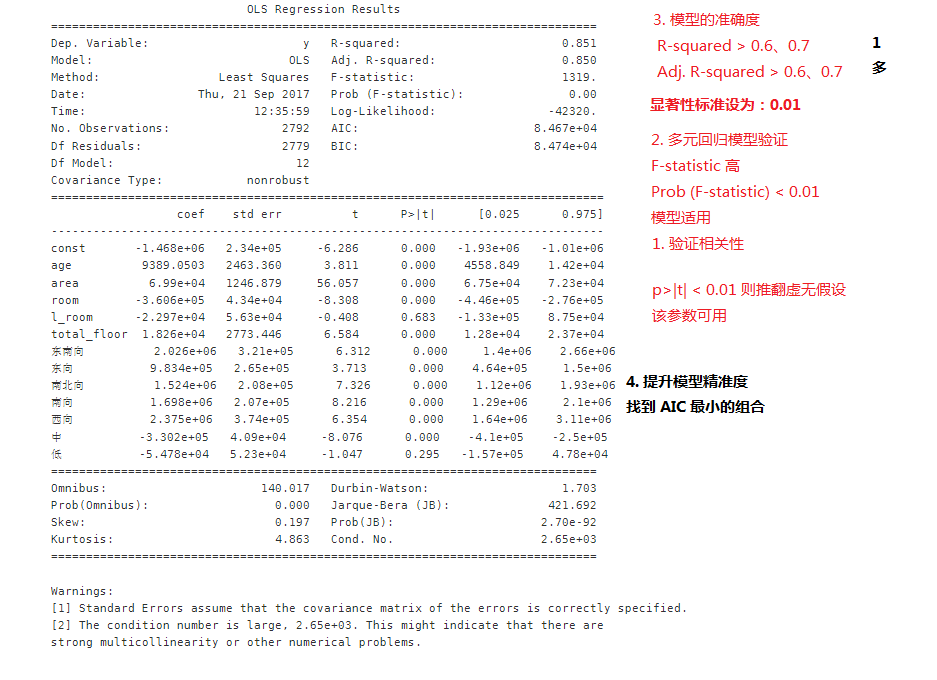
import statsmodels.api as smX2 = sm.add_constant(X)est = sm.OLS(Y, X2)est2 = est.fit()print(est2.summary())

predictorcols = ['age', 'area', 'room', 'l_room', 'total_floor', '东南向', '东向','南北向', '南向', '西向', '中', '低']import itertoolsAICs = {}for k in range(1, len(predictorcols)+1): for variables in itertools.combinations(predictorcols, k): predictor1 = X[list(variables)] predictor2 = sm.add_constant(predictor1) est = sm.OLS(Y, predictor2) res = est.fit() AICs[variables] = res.aic from collections import Counterc = Counter(AICs)c.most_common()[::-10]

比全部抛进去准确了 6W
转载地址:https://lipenglin.blog.csdn.net/article/details/78051104 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
逛到本站,mark一下
[***.202.152.39]2024年04月11日 15时39分59秒
关于作者

喝酒易醉,品茶养心,人生如梦,品茶悟道,何以解忧?唯有杜康!
-- 愿君每日到此一游!
推荐文章
攻防世界web进阶区ics-04详解
2019-04-30
攻防世界web进阶区Cat详解
2019-04-30
攻防世界web进阶区bug详解
2019-04-30
攻防世界web进阶区ics-07详解
2019-04-30
攻防世界web进阶区unfinish详解
2019-04-30
攻防世界web进阶区i-got-id-200超详解
2019-04-30
sql注入总结学习
2019-04-30
leetcode46 全排列
2019-04-30
leetcode121 买卖股票的最佳时机
2019-04-30
leetcode 122 买卖股票的最佳时机II
2019-04-30
leetcode 309 最佳买卖股票含冷冻期
2019-04-30
leetcode 714 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
2019-04-30
leetcode3 无重复字符的最长子串
2019-04-30
leetcode 76 最小覆盖子串
2019-04-30
leetcode 1143. 最长公共子序列
2019-04-30
leetcode 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
2019-04-30
智能体 Intelligent Agent
2019-04-30
Network Compression网络压缩(一)
2019-04-30
GAN系列(零)—— GAN的发展(两条路线)
2019-04-30
Python 之 histogram直方图
2019-04-30
