
LeetCode C++ 173. Binary Search Tree Iterator【二叉搜索树/栈/设计】中等
发布日期:2021-07-01 02:52:01
浏览次数:2
分类:技术文章
本文共 2867 字,大约阅读时间需要 9 分钟。
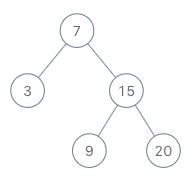
Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST. Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example:

BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root);iterator.next(); // return 3iterator.next(); // return 7iterator.hasNext(); // return trueiterator.next(); // return 9iterator.hasNext(); // return trueiterator.next(); // return 15iterator.hasNext(); // return trueiterator.next(); // return 20iterator.hasNext(); // return false
Note:
next()andhasNext()should run in averageO(1)time and usesO(h)memory, wherehis the height of the tree.- You may assume that
next()call will always be valid, that is, there will be at least a next smallest number in the BST whennext()is called.
题意:设计一个二叉搜索树迭代器,使用二叉搜索树的根结点初始化迭代器。假定调用 next() 时总是有效的,它会返回二叉搜索树的下一个最小的数。
思路1
二叉搜索树的中序遍历序列是单调递增的,我们先进行递归中序遍历,得到二叉搜索树的中序序列。然后返回下一个数即可。初始化使用 O ( n ) O(n) O(n) 时间和空间,next(), hasNext() 使用 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) 时间和空间。代码如下:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */class BSTIterator { private: vector inorders; int idx = 0; void inorder(TreeNode *root) { if (root) { inorder(root->left); inorders.push_back(root->val); inorder(root->right); } }public: BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) { inorder(root); } /** @return the next smallest number */ int next() { return inorders[idx++]; } /** @return whether we have a next smallest number */ bool hasNext() { return idx < inorders.size() ? true : false; }};/** * Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * BSTIterator* obj = new BSTIterator(root); * int param_1 = obj->next(); * bool param_2 = obj->hasNext(); */ 效率如下:
执行用时:116 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了11.68% 的用户内存消耗:25.9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了13.39% 的用户
思路2:关键是构建一个 O ( h ) O(h) O(h) 的最小存储栈。我们不进行事先的遍历,而是利用二叉树的迭代中序遍历,保存左子链,从而只使用 O ( h ) O(h) O(h) 的内存。注意:这里的 next(), hasNext() 的均摊复杂度为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) 。代码如下:
class BSTIterator { private: vector st;public: BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) { //O(logN) while (root) { st.push_back(root); root = root->left; } } /** @return the next smallest number */ int next() { TreeNode *t = st.back(); st.pop_back(); //中序遍历访问结点 int val = t->val; t = t->right; while (t) { st.push_back(t); t = t->left; } return val; } /** @return whether we have a next smallest number */ bool hasNext() { return !st.empty(); }}; 效率如下:
执行用时:92 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了68.20% 的用户内存消耗:25.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了98.51% 的用户
转载地址:https://memcpy0.blog.csdn.net/article/details/108736104 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
不错!
[***.144.177.141]2024年04月18日 18时37分09秒
关于作者

喝酒易醉,品茶养心,人生如梦,品茶悟道,何以解忧?唯有杜康!
-- 愿君每日到此一游!
推荐文章
Azkaban体系结构
2019-05-01
机器学习之重头戏-特征预处理
2019-05-01
synchronized底层实现及锁的升级、降级
2019-05-01
PermGen space-永久区内存溢出
2019-05-01
Maven继承和聚合
2019-05-01
Apache Kafka:优化部署的 10 种最佳实践
2019-05-01
Leetcode 35. 搜索插入位置 c#
2019-05-01
[9] JMeter-常用函数的使用
2019-05-01
[12] JMeter-结果分析之图形图表
2019-05-01
has been blocked by CORS policy: Response to preflight request doesn‘t pass access control check 报错
2019-05-01
使用aspose.words 18.6实现pdf文档转换
2019-05-01
Java数组详解
2019-05-01
vs中动态DLL与静态LIB工程中加入版本信息的方法
2019-05-01
大数据分析技术与应用一站式学习(值得收藏)_v20200418
2019-05-01
Qt 在windows下的串口读写
2019-05-01
SpringApplication执行流程
2019-05-01
自定义Starter
2019-05-01
分布式事务原理探究(一)
2019-05-01