
本文共 3140 字,大约阅读时间需要 10 分钟。
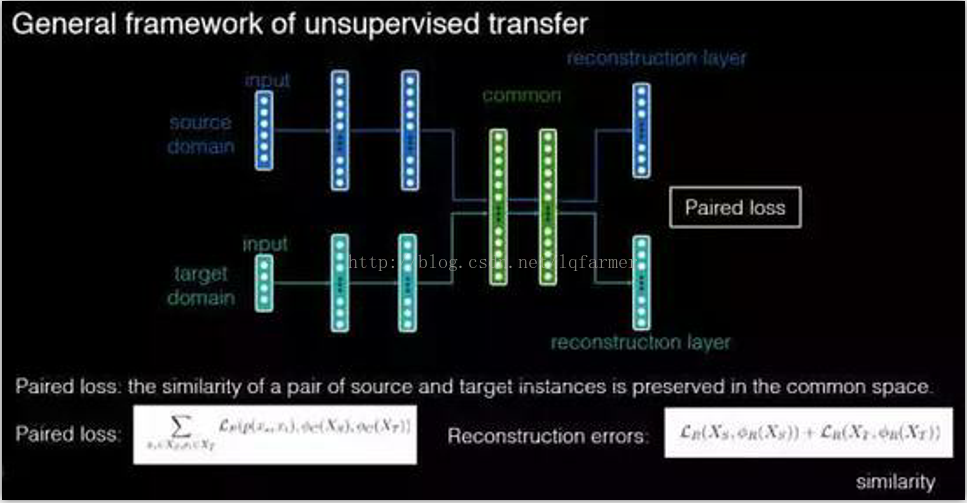
之前,在文章《》中,介绍了关于Domain Adaptation的相关基础知识,并没有深入介绍Domain Adaptation相关算法的原理。今天,分享一个与Domain Adaptation相关的视频(附PPT),感兴趣的同学可以下载。
视频及PPT下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1i5HuusX 密码: 公众号回复“da”即可获得密码
Domain Adaptation相关的经典论文分享。按原理分类:
Covariate Shift Based:
[1] James Heckman. Sample Selection Bias as a Specification Error. 1979. Nobel prize-winning paper which introduced Sample Selection Bias.
[2] Arthur Gretton et al. Covariate Shift by Kernel Mean Matching. 2008. Describes a procedure for computing the optimal source weights, given infinite unlabeled data and a universal kernel. Also provides target error bounds when learning under the labeled source distribution.
[3] Corinna Cortes et al. Sample Selection Bias Correction Theory. 2008. Analyzes the case when we have only finite unlabeled data, so that we cannot determine the optimal weights exactly. This leads to a bias when learning from
the source domain.
[4] Steffen Bickel. Discriminative Learning under Covariate Shift. 2009. Introduces the logistic regression model for learning source weights directly from unlabeled data.
Representation Learning Based:
[5] John Blitzer et al. Domain Adaptation with Structural Correspondence Learning. 2006. Describes the projection-learning technique from this section.
[6] Shai Ben-David et al. Analysis of Representations for Domain Adaptation. 2007. Gives an early version of the discrepancy distance and its relation to adaptation error.
[7] John Blitzer et al. Domain Adaptation for Sentiment Classification. 2007. Describes an application of projection learning to sentiment classification. These are the results from the previous section.
[8] Yishay Mansour et al. Domain Adaptation: Learning Bounds and Algorithms. 2009. Generalizes the discrepancy distance to arbitrary losses and gives a tighter bound than above. Also describes techniques for learning instances weights to directly minimize discrepancy distance.
Feature Based Supervised Adaptation Based:
[9] T. Evgeniou and M. Pontil. Regularized Multi-task Learning. 2004.
[10] Hal Daume III. Frustratingly Easy Domain Adaptation. 2007. Describes the feature replication algorithm from this section.
[11] Kilian Weinberger et al. Feature Hashing for Large Scale Multitask Learning. 2009. Describes the feature hashing technique for handling millions of domains or tasks simultaneously.
[12] A. Kumar et al. Frustratingly Easy Semi-supervised Domain Adaptation. 2010.Shows how to incorporate unlabeled data in the feature replication framework.
Parameter Based Supervised Adaptation Based:
[13] Olivier Chapelle et al. A machine learning approach to conjoint analysis. 2005.
[14] Kai Yu et al. Learning Gaussian Processes from Multiple Tasks. 2005. Kernelized multi-task learning with parameters linked via GP prior.
[11] Ya Xue et al. Multi-task Learning for Classification with Dirichlet Process Priors. 2007. Learning with parameters linked via DP clustering.
[12] Hal Daume III. Bayesian Multitask Learning with Latent Hierarchies. 2009. Describes the latent hierarchical modeling.
往期精彩内容推荐:
更多精彩,点击公众号“往期内容”查看。
更多在NLP方面应用的经典论文、实践经验和最新消息,欢迎关注公众号“与NLP”或“DeepLearning_NLP”或扫描二维码添加关注。

转载地址:https://lqfarmer.blog.csdn.net/article/details/73611796 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
关于作者
