
本文共 10853 字,大约阅读时间需要 36 分钟。
目录
第七章 Web开发
7.3 请求参数处理
7.3.1 请求映射
7.3.1.1 Rest使用与原理
在一个方法上加注解@RequestMapping,来声明这个方法能处理什么请求,这个声明过程就是请求映射。
- Rest风格支持:使用Http请求方式的动词来表示对资源的操作
- 以前:/getUser 获取用户 /deleteUser 删除用户 /editUser 修改用户 /saveUser 保存用户
- 现在:/user(路径都是一样的) GET-获取用户 DELETE-删除用户 PUT-修改用户 POST-保存用户
- Rest风格实现的核心Filter:HiddenHttpMethodFilter
-
WebMvcAutoConfiguration类中有一个方法hiddenHttpMethodFilter()
-
OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter要继承HiddenHttpMethodFilter
-
用法:表单method=post,使用post请求方式。隐藏域_method=put
-
SpringBoot中手动开启
-
@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBean({HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class})@ConditionalOnProperty( prefix = "spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter", name = {"enabled"})public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() { return new OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter();} public class OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter extends HiddenHttpMethodFilter implements OrderedFilter {} public class HiddenHttpMethodFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter { private static final List ALLOWED_METHODS; public static final String DEFAULT_METHOD_PARAM = "_method"; private String methodParam = "_method";//后续可以在自定义的组件中修改这个参数实现自定义名字 //允许put、delete、patch static { ALLOWED_METHODS = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(HttpMethod.PUT.name(), HttpMethod.DELETE.name(), HttpMethod.PATCH.name())); } protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException { HttpServletRequest requestToUse = request; //需要是post请求方式,参数是_method if ("POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.exception") == null) { //获取_method属性的值 String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam); if (StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue)) { //都会转为大写,因此表单中填属性值时大小写均可 String method = paramValue.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH); if (ALLOWED_METHODS.contains(method)) { requestToUse = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter.HttpMethodRequestWrapper(request, method); } } } //放行新的请求方式 filterChain.doFilter((ServletRequest)requestToUse, response); }} private static class HttpMethodRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper { private final String method; public HttpMethodRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request, String method) { super(request); this.method = method;//保存新的请求方式,即从_method中得到的值 } public String getMethod() { return this.method;//然后把这个新的请求方式返回 }} 具体实现:
spring: mvc: hiddenmethod: filter: enabled: true #手动开启该功能


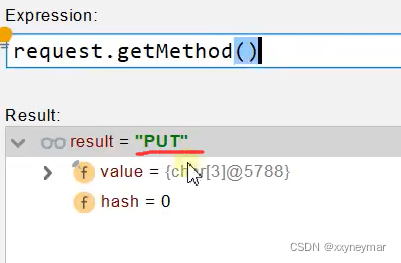
- Rest原理(表单提交使用Rest的时候):总体来看就是用一个过滤器把原生请求的getMethod方法重写了,换成了新的请求方式。
- 表单提交会带上_method=PUT
- 请求过来被HiddenHttpMethodFilter拦截
- 请求是否正常,并且是POST
-
获取到_method的值
-
兼容以下请求;PUT.DELETE.PATCH
- 原生request(post),包装模式requesWrapper重写了getMethod方法,返回的是_method的值。
- 过滤器链放行的时候用wrapper。以后的方法调用getMethod是调用requesWrapper的。
-
- 请求是否正常,并且是POST
- Rest如果使用客户端工具
- 如PostMan可以直接发送put、delete等请求方式,就不需要这个Filter了。此时请求一开始就不是post了,也就没有进入后续方法的条件。

- SpringBoot中因此也产生了新注解,但其实底层实现的就是@RequestMapping
- @GetMapping("/user")
- @PostMapping("/user")
- @PutMapping("/user")
- @DeleteMapping("/user")
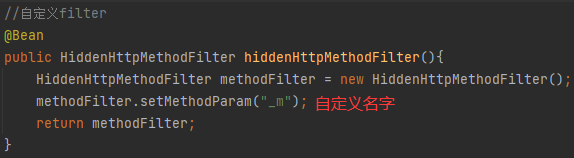
- 如何修改_method,改成自定义的
- 底层实现是如果没有手动写HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class这个组件,那么默认就会自动创建一个这个组件,默认判断的就是_method
- 可以自己定义一个HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class。
7.3.1.2 请求映射原理
底层还是SpringMVC,所有请求都会到DispatcherServlet。
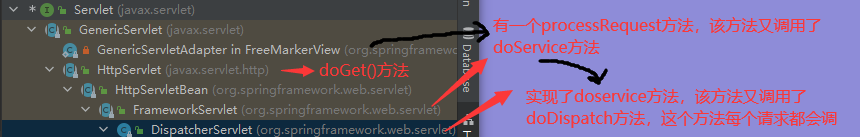
SpringMVC功能分析都从org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet->doDispatch()
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { //传入原生的request、response HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;//是不是一个文件上传请求 WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);//异步管理器 try { try { ModelAndView mv = null; Object dispatchException = null; try { //checkMultipart检查是否是文件上传请求 processedRequest = this.checkMultipart(request); //如果是文件上传请求,进行一个转化 multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request; //找到当前请求使用哪个Handler(Controller的方法)处理 mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest); getHandler方法中,handlerMapping:处理器映射。/xxx->>xxxx,即各种映射规则。
@Nullableprotected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this.handlerMappings != null) { Iterator var2 = this.handlerMappings.iterator(); while(var2.hasNext()) { HandlerMapping mapping = (HandlerMapping)var2.next(); HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } } return null;} 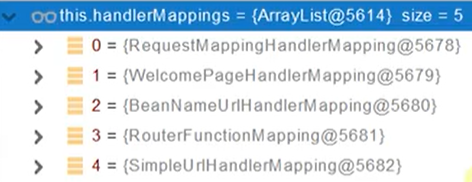
RequestMappingHandlerMapping:保存了所有@RequestMapping注解和handler的映射
规则。
比如请求调用getUser()过程,先按照写的"/user"找到四种可能的(get、post、delete、put),
再从这四种中找到最匹配的那个。注意因此要求对同一种请求,只能有一个最匹配的处理方
式。
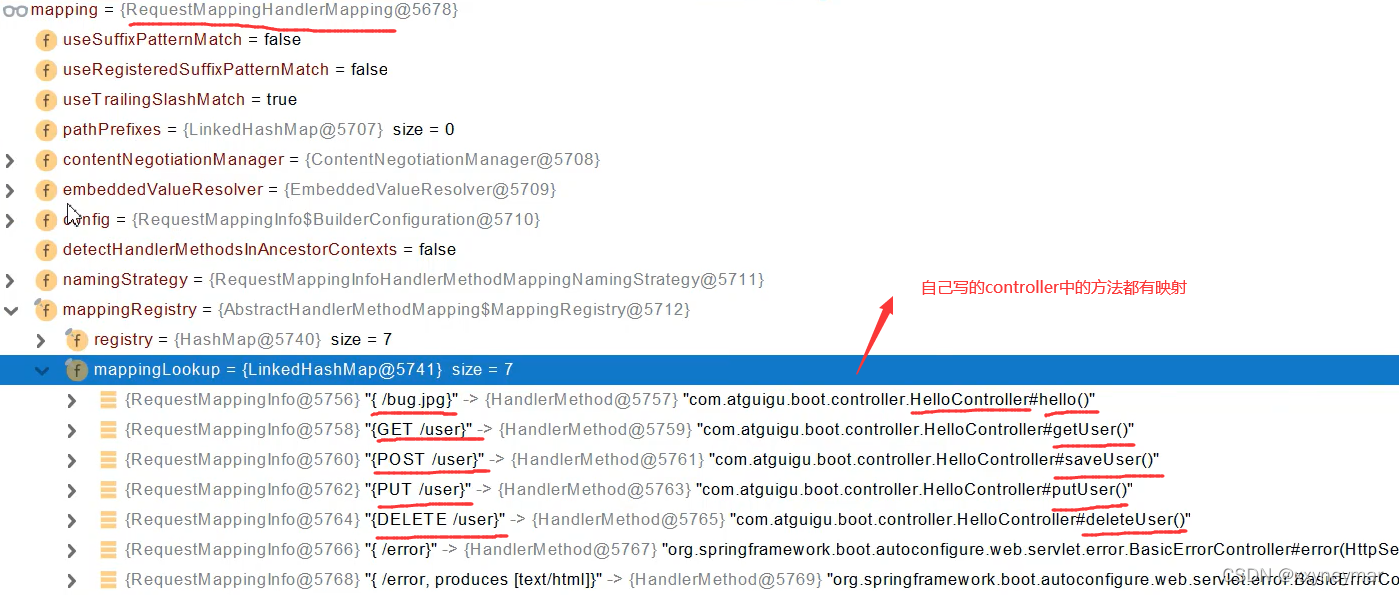
应用一启动,SpringMVC自动扫描所有的controller并解析注解,把这些注解信息全部保存到handlerMapppings中。然后挨个找所有得请求映射,看哪个可以处理请求。
- 所有的请求映射都在handlerMappings中
- SpringBoot自动配置欢迎页的WelcomePageHandlerMapping 。访问"/"能访问到index.html
- SpringBoot自动配置了默认的RequestMappingHandlerMapping
-
请求进来,挨个尝试所有的HandlerMapping看是否有请求信息
- 如果有就找到这个请求对应的handler
- 如果没有就比较下一个 HandlerMapping
- 我们需要一些自定义的映射处理,我们也可以自己给容器中放HandlerMapping,自定义 HandlerMapping
7.3.2 普通参数与基本注解
7.3.2.1 注解
@PathVariable:接受请求路径中占位符的值。可以将URL占位符参数{xxx}绑定到处理器类的方法形参中@PathVariable(“xxx“)。
①可以一个个取路径中的值
②也可以把路径中的所有参数及其值放在一个Map<String,String>中
@RequestHeader:获取请求头中的数据,通过指定参数value的值来获取请求头中指定的参数值。
①可以一个个取请求头中的参数
②也可以直接把请求头中的所有参数放在一个Map<String,String>中
@ModelAttribute:运用在参数上,会将客户端传递过来的参数按名称注入到指定对象中,并且会将这个对象自动加入ModelMap中,便于View层使用;被@ModelAttribute注释的方法会在此controller的每个方法执行前被执行 ,如果有返回值,则自动将该返回值加入到ModelMap中。
@RequestParam:将请求参数绑定到控制器的方法参数上(是springmvc中接收普通参数的注解)
①可以一个个取请求参数
②也可以直接把所有请求参数放在一个Map<String,String>中
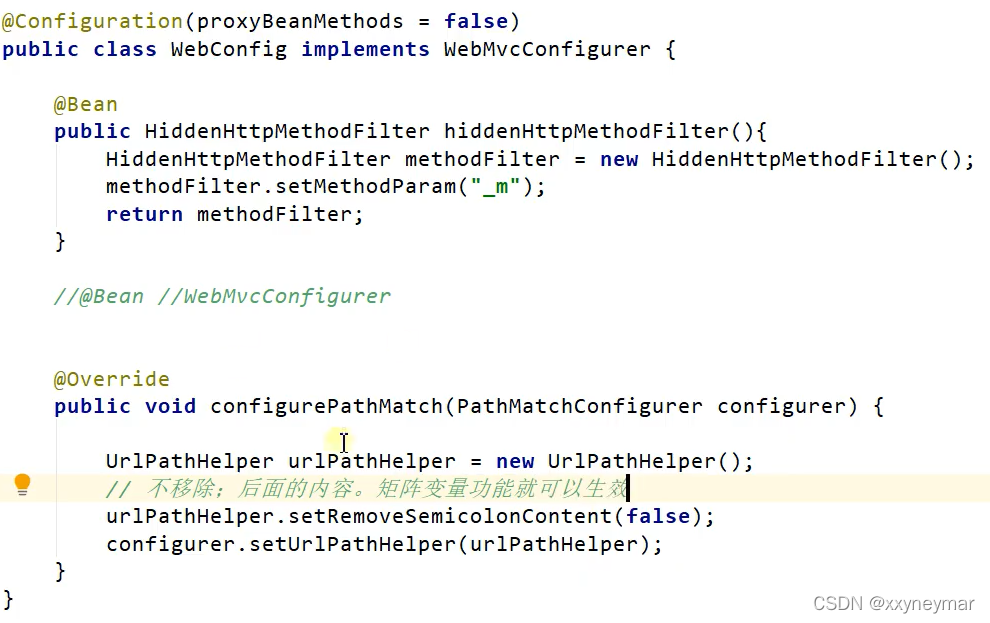
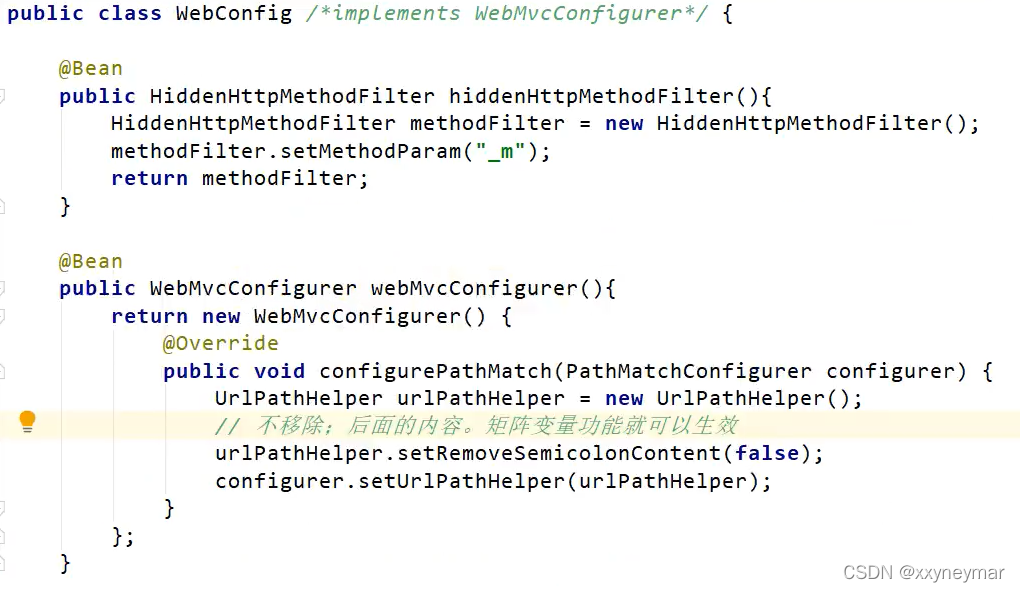
@MatrixVariable:注解拓展了URl请求地址的功能。使用@MatrixVariable注解时多个变量可以使用;(分号)分隔。矩阵变量绑定在路径变量中。SpringBoot默认关闭这个功能,要自己手动开启。

原理:WebMvcAutoConfiguration类中的静态类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter中有一个
方法configurePathMatch(),再查看类UrlPathHelper,里面有一个属性
removeSemicolonContent,当设置为true时会把URL中";"后面的去掉,而默认为true。需要
自定义规则:@Configuration + 实现WebMvcConfigurer接口来来自定义规则。
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) { if (this.mvcProperties.getPathmatch().getMatchingStrategy() == MatchingStrategy.PATH_PATTERN_PARSER) { configurer.setPatternParser(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.pathPatternParser); } configurer.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(this.mvcProperties.getPathmatch().isUseSuffixPattern()); configurer.setUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this.mvcProperties.getPathmatch().isUseRegisteredSuffixPattern()); this.dispatcherServletPath.ifAvailable((dispatcherPath) -> { String servletUrlMapping = dispatcherPath.getServletUrlMapping(); if (servletUrlMapping.equals("/") && this.singleDispatcherServlet()) { UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper(); urlPathHelper.setAlwaysUseFullPath(true); configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper); } });} 
@Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false )@Import({WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class})@EnableConfigurationProperties({WebMvcProperties.class, WebProperties.class})@Order(0)public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer, ServletContextAware {}public interface WebMvcConfigurer { default void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) { }} 第一种实现WebMvcConfigurer接口方式:直接让配置类实现该接口,然后重写方法。
第二种实现WebMvcConfigurer接口方式:直接在容器中放一个这个类型的组件。
@CookieValue:用来获取Cookie中的值。
@RequestBody:用来接收前端传递给后端的json字符串中的数据的(请求体中的数据的),所以只能发送POST请求。GET方式无请求体,所以使用@RequestBody接收数据时,前端不能使用GET方式提交数据,而是用POST方式进行提交。@RequestBody与@RequestParam()可以同时使用,@RequestBody最多只能有一个,而@RequestParam()可以有多个。注:一个请求,只有一个RequestBody;一个请求,可以有多个RequestParam。
@RequestAttribute:获取request域属性,即获取HTTP的请求(request)对象属性值,用来传递给控制器的参数。
@ResponseBody:作用是将java对象转为json格式的数据。将controller的方法返回的对象通过适当的转换器转换为指定的格式之后,写入到response对象的body区。
比如有以下请求:
get请求:

post请求:
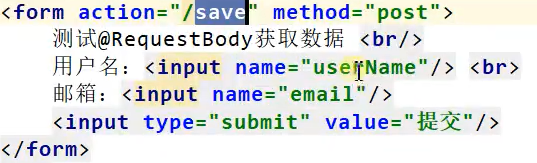
@RestControllerpublic class ParameterTestController { // car/2/owner/zhangsan @GetMapping("/car/{id}/owner/{username}") public Map getCar(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("username") String name, @PathVariable Map pv, @RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent, @RequestHeader Map header, @RequestParam("age") Integer age, @RequestParam("inters") List inters, @RequestParam Map params, @CookieValue("_ga") String _ga, @CookieValue("_ga") Cookie cookie){ Map map = new HashMap<>();// map.put("id",id);// map.put("name",name);// map.put("pv",pv);// map.put("userAgent",userAgent);// map.put("headers",header); map.put("age",age); map.put("inters",inters); map.put("params",params); map.put("_ga",_ga); System.out.println(cookie.getName()+"===>"+cookie.getValue()); return map; } @PostMapping("/save") public Map postMethod(@RequestBody String content){ Map map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("content",content); return map; } //1、语法: 请求路径:/cars/sell;low=34;brand=byd,audi,yd //2、SpringBoot默认是禁用了矩阵变量的功能 // 手动开启:原理。对于路径的处理。UrlPathHelper进行解析。 // removeSemicolonContent(移除分号内容)支持矩阵变量的 //3、矩阵变量必须有url路径变量才能被解析 @GetMapping("/cars/{path}") public Map carsSell(@MatrixVariable("low") Integer low, @MatrixVariable("brand") List brand, @PathVariable("path") String path){ Map map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("low",low); map.put("brand",brand); map.put("path",path); return map; } // url:/boss/1;age=20/2;age=10 @GetMapping("/boss/{bossId}/{empId}") public Map boss(@MatrixVariable(value = "age",pathVar = "bossId") Integer bossAge, @MatrixVariable(value = "age",pathVar = "empId") Integer empAge){ Map map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("bossAge",bossAge); map.put("empAge",empAge); return map; }} @Controllerpublic class RequestController { @GetMapping("/goto") public String gotoPage(HttpServletRequest request) { request.setAttribute("msg","成功了"); //向请求作用域中加入参数 request.setAttribute("code",200); return "forward:/success"; //转发到/success } @ResponseBody @GetMapping("/success") public Map success(@RequestAttriubute("msg") String msg, @RequestAttriubute("code") Integer code, HttpServletRequest request) { Object msg1 = request.getAttribute("msg"); Map map = new HashMap<>; map.put("reqMethod_msg",msg1); map.put("annnotation_masg",msg); return map; }} PS:根据尚硅谷视频整理,如有侵权,联系删除。
转载地址:https://blog.csdn.net/xxyneymar/article/details/122562779 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
关于作者
